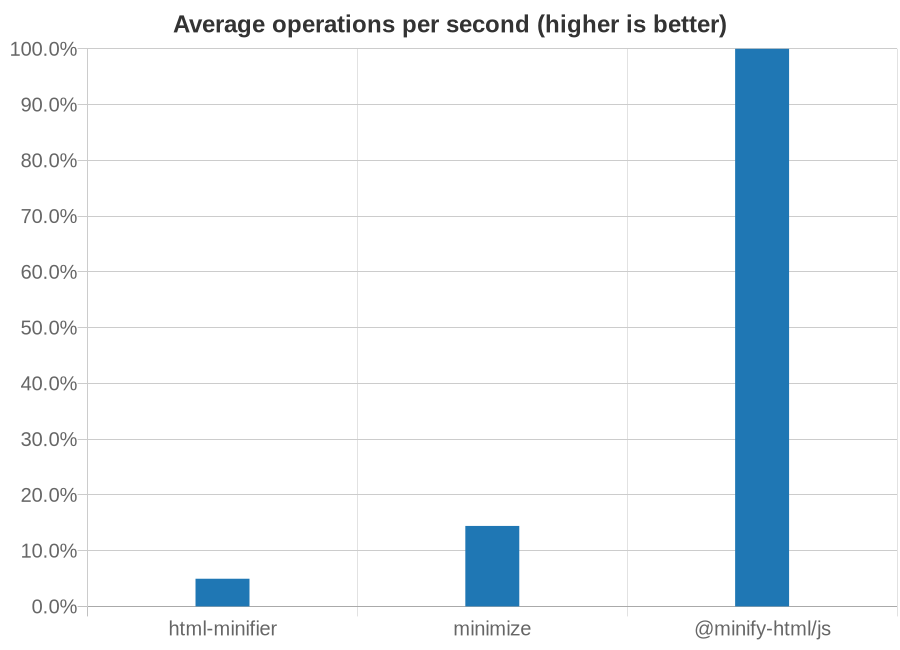
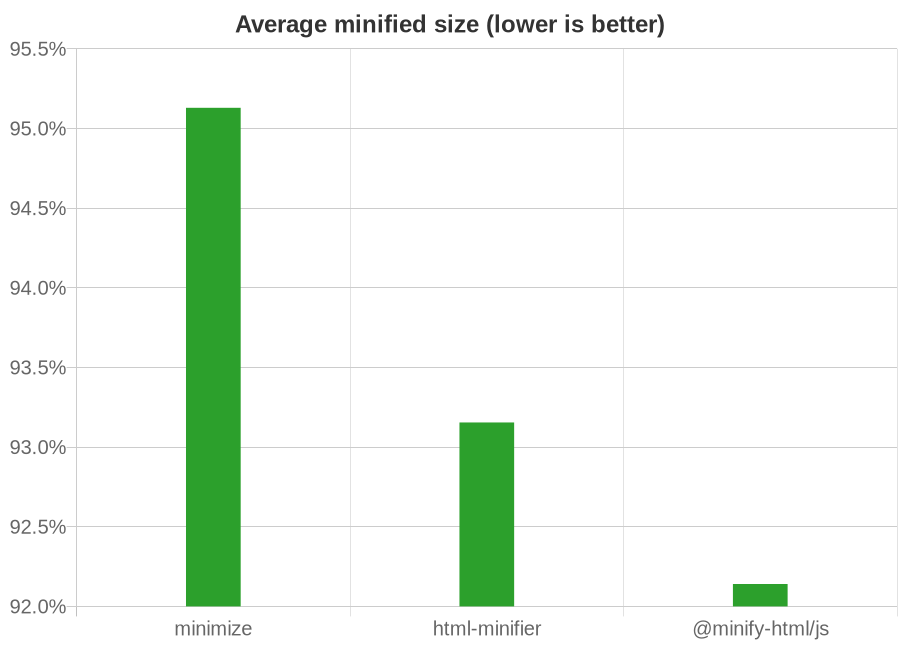
 ## Usage
## Usage
Hello, world!
", cfg); // Alternatively, minify in place to avoid copying. const source = Buffer.from("Hello, world!
"); // This is a Buffer representing a slice of `source`, not newly allocated memory. const minified = minifyHtml.minifyInPlace(source, cfg); ``` minify-html is also available for TypeScript: ```ts import * as minifyHtml from "@minify-html/js"; import * as fs from "fs"; const cfg = minifyHtml.createConfiguration({ minifyJs: false, minifyCss: false }); const minified = minifyHtml.minify("Hello, world!
", cfg); // Or alternatively: const minified = minifyHtml.minifyInPlace(fs.readFileSync("source.html"), cfg); ```Hello, world!
", cfg); } catch (SyntaxException e) { System.err.println(e.getMessage()); } // Alternatively, minify in place: assert source instanceof ByteBuffer && source.isDirect(); MinifyHtml.minifyInPlace(source, cfg); ```Hello, world!
", minify_js=False, minify_css=False) except SyntaxError as e: print(e) ```Hello, world!
", { :minify_js => false, :minify_css => false }) ```| Before | After |
|---|---|
|
```html
↵ ··The·quick·brown·fox↵ ··jumps·over·the·lazy↵ ··dog.↵ ``` |
```html
·The·quick·brown·fox·jumps·over·the·lazy·dog.· ``` |
| Before | After |
|---|---|
```html
|
```html
|
| Before | After |
|---|---|
|
```html
↵ ··Hey,·I·just·found↵ ··out·about·this·cool·website!↵ ··[1]↵ ``` |
```html
Hey,·I·just·found↵ ··out·about·this·cool·website!↵ ··[1] ``` |
↵ ··Hey,·I·just·found↵ ··out·about·this·cool·website!↵ ··[1]↵
``` ###### After ```htmlHey,·I·just·found·out·about·this·cool·website!·[1]
```